In-depth analysis of why cryptocurrencies are gaining popularity in third world countries

Blockchain-based encrypted digital currencies are gradually being applied worldwide as a disruptive payment method. People can complete transactions anywhere in the world solely through the Internet, freeing themselves from geographical constraints and factors such as traditional fiat currencies and sovereign governments.
Table of Contents
When it comes to active regions in the cryptocurrency field, people usually associate it with technologically advanced developed countries in Europe and the United States, as well as emerging markets in Asia. However, it is worth noting that many third world countries in Asia, Africa, and South America have shown a growing interest in digital currencies.
The cryptocurrency trading on the well-known over-the-counter platform LocalBitcoins can be seen as a microcosm of the global cryptocurrency market. By looking at the trading volume, we can see the demand for cryptocurrencies in specific countries and regions. According to CoinDance data, since 2018, Venezuela's Bitcoin trading volume on LocalBitcoins has been second only to Russia, on par with the United States. The trading volume in Nigeria has been comparable to that of China, the UK, and Europe for most of the time.
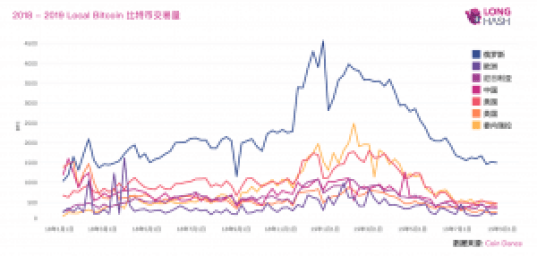
Some well-known projects have also discovered the huge potential of cryptocurrencies in third world countries and have actively entered these markets. Dash's African team, centered in Nigeria, continuously attracts more merchants and consumers in Nigeria and surrounding areas to adopt Dash through television, brochures, and live events. Stellar has helped integrate the Stellar network with payment service providers and telecommunications companies in Nigeria, Ghana, Kenya, and India, allowing users to experience convenient and low-cost transfers on the Stellar chain. The stablecoin project Reserve, launched in 2019, is being implemented in Venezuela and Angola, introducing stablecoin applications.
Persistently High Inflation Rates
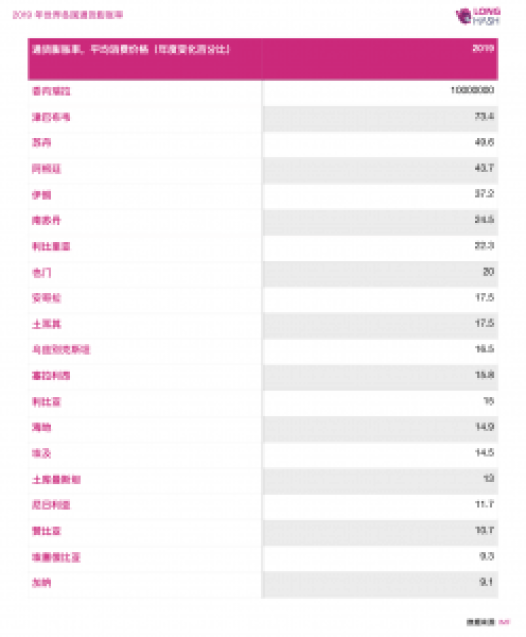
According to the IMF's 2019 global inflation rate statistics, within the scope of countries with available data, there are 9 countries worldwide with inflation rates exceeding 20%, and 19 countries with inflation rates above 10%. In these high inflation countries, holding the local currency means a significant devaluation of purchasing power, and alternative investment options such as foreign exchange, gold, and other hedging methods have high entry barriers, making it difficult to obtain through traditional financial channels. In countries with severe inflation, the shift towards Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies for transactions is foreseeable.
Limited Development of Traditional Financial Services
In underdeveloped countries, the development of banks and other traditional financial services is not well established, with low penetration rates. However, the penetration of mobile phones precedes the development of financial services, leading to a highly developed mobile financial services industry. Taking Africa as an example, according to a survey by the University of Nairobi in Kenya, the current mobile phone penetration rate in Africa has exceeded 80%, and the number of people using mobile payments is three times that of those with bank accounts, becoming the second most popular payment method after cash. The widespread use of mobile payments and the internet provide a good foundation for the development of cryptocurrencies. Due to the lack of traditional financial infrastructure and the prevalence of mobile payments, more ordinary people have the opportunity to benefit from the efficient and low-cost transfer fees and security features of cryptocurrencies, enjoying the convenience of new financial services.
Government Openness
In countries plagued by long-term severe inflation, government monetary and fiscal policies have become ineffective. In such predicaments, many countries like Venezuela, Argentina, Nigeria, Zimbabwe, and Uganda have shown a relatively open attitude towards cryptocurrencies or have not yet imposed restrictions, and generally express support for the application of blockchain technology.
Although governments of countries facing economic crises may adopt a friendly attitude towards cryptocurrencies, it does not mean that there are no regulatory risks in the future. With the accelerated development of cryptocurrencies and their industries, these governments may introduce more comprehensive regulatory measures or policies towards cryptocurrencies.
For example, in February 2019, Venezuela issued the "Constitutional Decree on the Integral System of Crypto Assets," which requires the establishment of the national agency SUNACRIP to regulate all activities related to cryptocurrencies such as mining, custody, trading, and issuance. Mining without a permit may result in fines ranging from $6,000 to $18,000 and confiscation of mining machines. For blockchain projects, a country's stance on digital currencies determines their strategic choices, and the tightening of regulatory policies, as seen in Venezuela, can pose significant risks to the subsequent operation of projects.
Summarizing the above, we can see from data and practical implementations that in third world countries with high inflation rates, open government attitudes towards cryptocurrencies, and high mobile scene penetration rates, cryptocurrencies often receive favorable attention.
If people's demand for cryptocurrencies also follows a hierarchy similar to Maslow's hierarchy of needs, then developed countries and third world countries have subtle differences in demand. In developed countries like the United States with financial dominance, people holding fiat currencies have already benefited from the efforts of central banks to stabilize the value of the currency and have the endorsement of developed economies on the currency's value, making fiat currency stable and reliable, and the standard for measuring cryptocurrency volatility. Geeks from developed countries do not need to worry about finding a stable currency with usability; they are more inclined to see the beauty of code, the Hayekian road, and the peak of the Tower of Babel in cryptocurrencies—dedicated to building more anonymous algorithms, sophisticated community governance structures, and demanding Tokenize Everything.
Meanwhile, citizens in third world countries have more fundamental and practical desires for cryptocurrencies, such as stable measures of value, store of value, maintaining purchasing power, and a general equivalent that will not be deprived, to avoid the loss of purchasing power due to the weakening of the national currency system, and the policy squeeze of the US dollar-centric economic system on the country. In addition, blockchain and cryptocurrencies have brought a series of fast, low-cost financial services that were difficult to obtain before. From Silicon Valley engineers to workers in Zimbabwe, everyone can benefit from cryptocurrencies according to their needs, which is its unique charm.
This article was originally published by our partner LONGHASH
Related Readings
- Sports live streaming platform introduces FanChain for token economics
- CME Bitcoin index provider obtains the EU's first crypto license
Join now to get the most comprehensive information on financial technology, blockchain insights, and industry examples!
Related
- AI replacing human reviewers, TikTok begins massive layoffs starting from Malaysia
- VanEck ventures into crypto venture capital, raising $30 million to invest in tokenization and stablecoin platforms
- More security concerns with re-pledging! Symbiotic's Twitter account hacked for phishing, EIGEN investors rushing to sell locked tokens